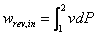Energy saving - Installing high efficiency motor

The electric power required for the air compressor can be expressed as, We can see that the electric power depends on the efficiency of the electric motor, thus, to install high efficiency motor we can save the energy as shown in the following equations, where: rated power = nominal power of the motor listed on its label (the power the motor delivers at full load) load factor = the fraction of rate power at which the motor normally operates The energy saving by replacing a motor by a high-efficiency motor can be calculated from, Normally, the efficiency of a motor ranges between 70% to 96%. The loss is usually in the form of heat. Load factor also plays an important part in heat generation. Normally, high heat level is generated during part loading of a compressor. Important considerations in the selection of a motor for a compressor Operating profile of a compressor i.e. load vs time Efficiency of the motor at part-load conditions Efficiency of the motor at full-load conditions One i...