Energy saving - Using outside air for compressor intake
The power consumed by a compressor is proportional to the specific volume, which is proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas at a given pressure. It is also clear that the compressor work is directly proportional to the inlet temperature of air. Therefore, the lower the inlet temperature of the air, the smaller the compressor work. Then the power reduction factor, which is the fraction of compressor power reduced as a result of taking intake air from the outside, becomes
freduction = (Wcomp, inside - Wcomp, outside) / Wcomp, inside
freduction = (Tinside - Toutside) / Tinside
freduction = 1 - (Toutside/Tinside)
where Tinside and Toutside are the absolute tempertaure (in K or R) of the ambient air inside and outside the facility, respectively. Thus reducing the absolute inlet temperature by 5%, for example, will reduce the compressor power input by 5%. As a rule of thumb, for a specified amount of compressed air, the power consumption of the compressor decreases (or, for a fixed power input, the amount of compressed air increases) by 1% for each 3oC drop in the temperature of the inlet air to the compressor.
Compressors are usually located inside the production facilities or in adjacent shelters specifically built outside these facilities. The intake air is normally drawn from inside the building or the shelter. But in many locations the air temperature in the building is higher than the outside air temperature, because of space heaters in the winter and the heat given up by a large number of mechanical and electrical equipment as well as furnaces year round.
The temperature rise in the shelter is also due to the heat dissipation from the compressor and its motor. The outside air is generally cooler and thus denser than the air in the compressor room even on hot summer days. Therefore, it is advisable to install and intake duct to the compressor inlet so that the air is supplied directly from the outside of the building instead of the insides. This will reduce the energy consumption of the compressor since it takes less energy to compress a specified amount of cool air than the same amount of warm air. Compressing the warm air in a building in winter also wastes the energy used to heat the air.
Read more..
freduction = (Wcomp, inside - Wcomp, outside) / Wcomp, inside
freduction = (Tinside - Toutside) / Tinside
freduction = 1 - (Toutside/Tinside)
where Tinside and Toutside are the absolute tempertaure (in K or R) of the ambient air inside and outside the facility, respectively. Thus reducing the absolute inlet temperature by 5%, for example, will reduce the compressor power input by 5%. As a rule of thumb, for a specified amount of compressed air, the power consumption of the compressor decreases (or, for a fixed power input, the amount of compressed air increases) by 1% for each 3oC drop in the temperature of the inlet air to the compressor.
Compressors are usually located inside the production facilities or in adjacent shelters specifically built outside these facilities. The intake air is normally drawn from inside the building or the shelter. But in many locations the air temperature in the building is higher than the outside air temperature, because of space heaters in the winter and the heat given up by a large number of mechanical and electrical equipment as well as furnaces year round.
The temperature rise in the shelter is also due to the heat dissipation from the compressor and its motor. The outside air is generally cooler and thus denser than the air in the compressor room even on hot summer days. Therefore, it is advisable to install and intake duct to the compressor inlet so that the air is supplied directly from the outside of the building instead of the insides. This will reduce the energy consumption of the compressor since it takes less energy to compress a specified amount of cool air than the same amount of warm air. Compressing the warm air in a building in winter also wastes the energy used to heat the air.
Read more..
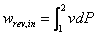
Comments